Orbital floor fractures may result when a blunt object which is of equal or greater diameter than the orbital aperture strikes the eye or on the cheek 1.
Best imaging for orbital floor and maxillary fracture.
Blunt force trauma tends to cause fractures along three lines of weakness in the mid face.
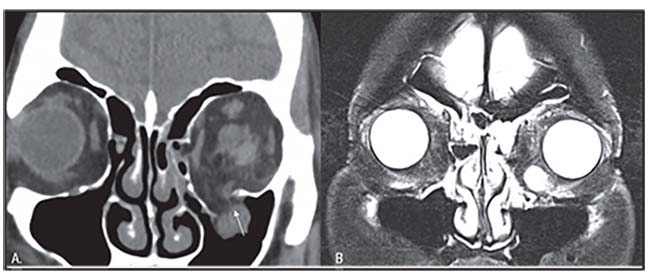
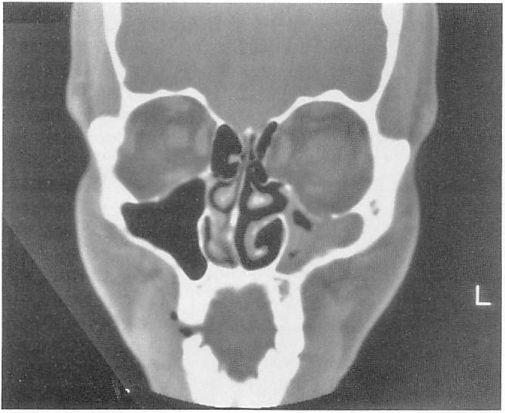
Orbital fat prolapses into the maxillary sinus and may be joined by prolapse of the inferior rectus muscle.
This patient had a significant vertical ocular motility disturbance.
One characteristic of all types of le fort fractures is the fracture of the.
Zygomatic sphenoid maxillary frontal lacrimal palatine and ethmoid.
Getting hit with a baseball or a fist often causes a orbital blowout fracture.
A retrospective study by bartoli et al of 301 orbital floor fractures found the most common symptom to be hypesthesia extending through the region of the maxillary nerve 32 9 of patients.
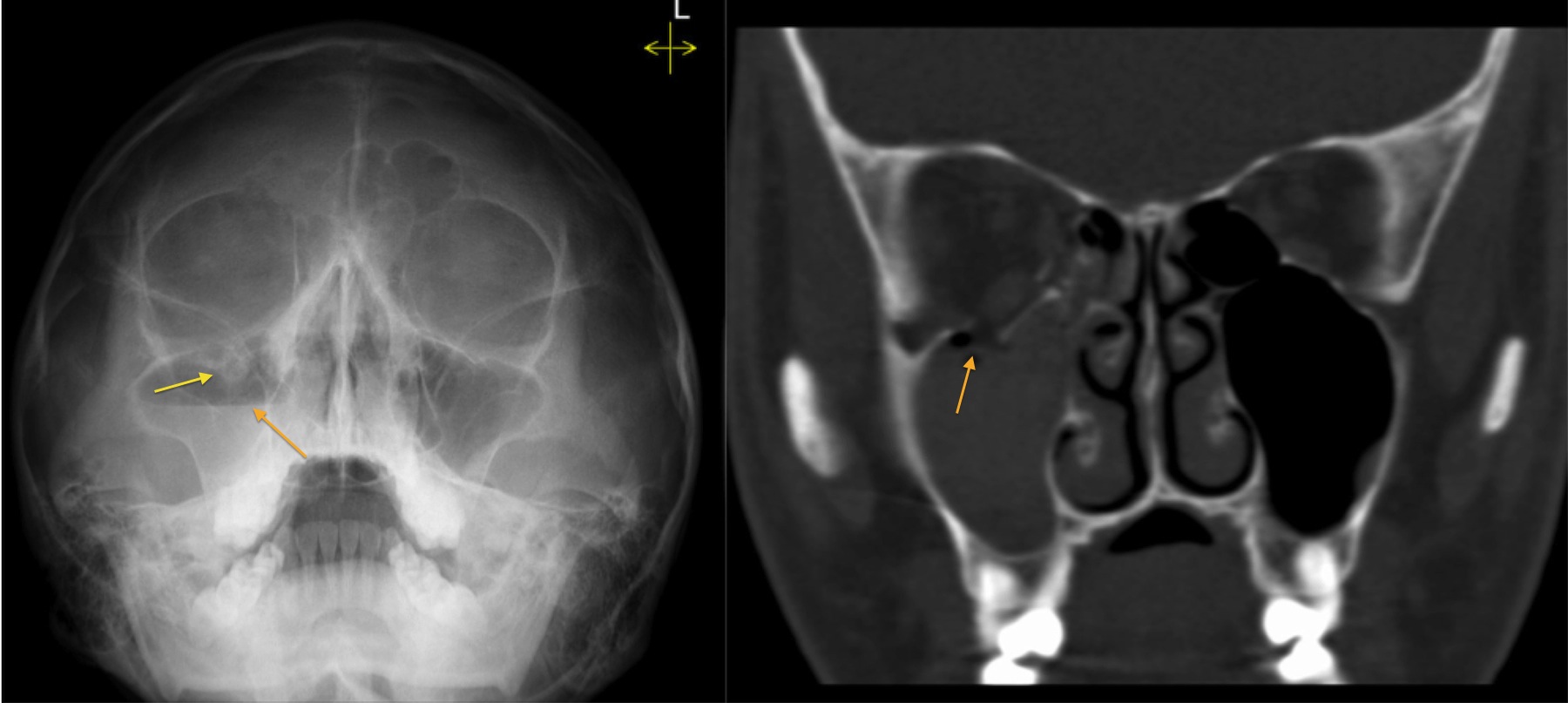
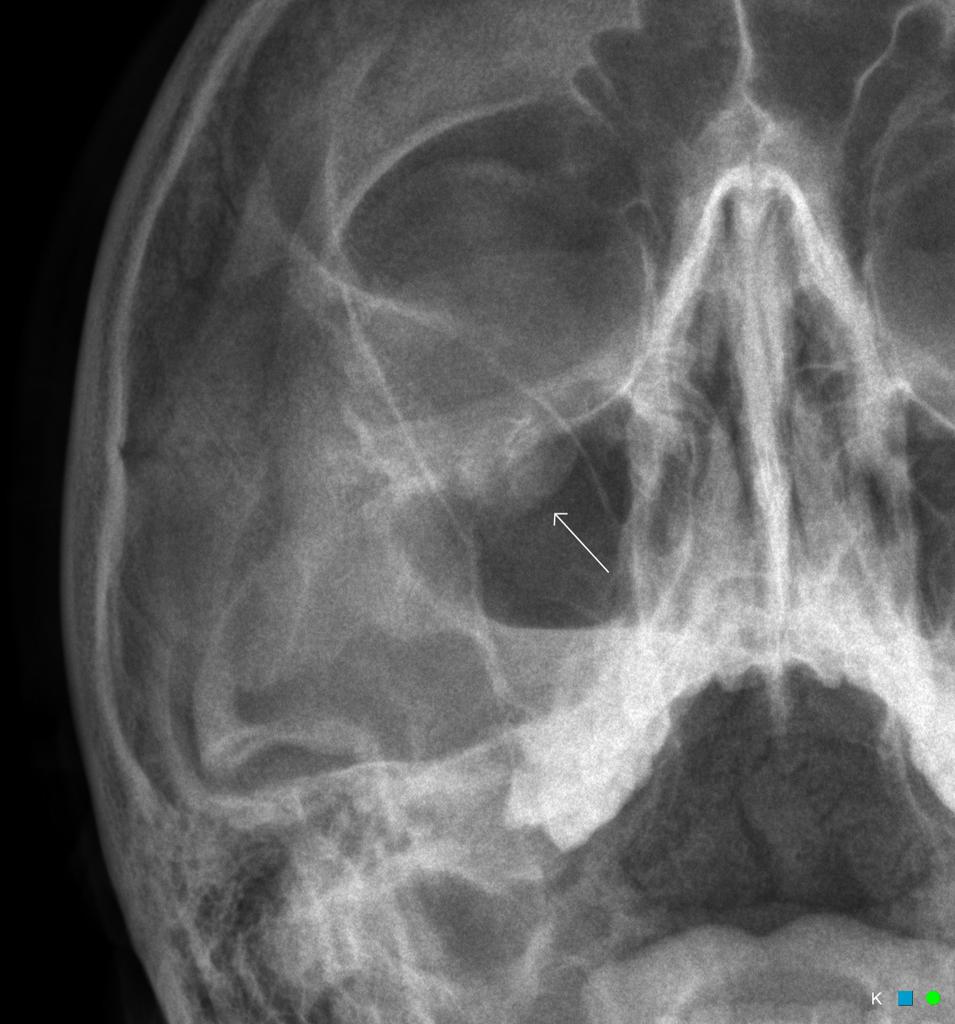
This is a rim fracture that extends into the lower socket.
Mid face le fort fractures.
Maxillary bones upper jaw.
Fractures of the orbit may be seen in different scenarios of direct and indirect trauma to the globe orbital facial or cranial bones.
However rare cases of nontraumatic orbital blowout fractures have been reported secondary to sneezing or nose blowing we describe a case of a nontraumatic orbital floor fracture that was diagnosed on imaging and affected patient management.
The usual mechanism is a blow to the eye with the forces being transmitted by the soft tissues of the orbit downward to the thin floor of the orbit.
Waters view best displays inferior orbital rims nasoethmoidal bones and maxillary sinuses.
Another common fracture is the orbital floor fracture or blowout fracture.
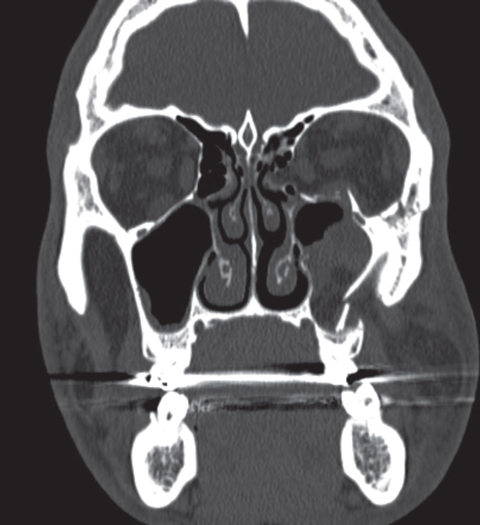
Note the relatively small amount of herniated tissue and the air fluid level in the maxillary sinus.
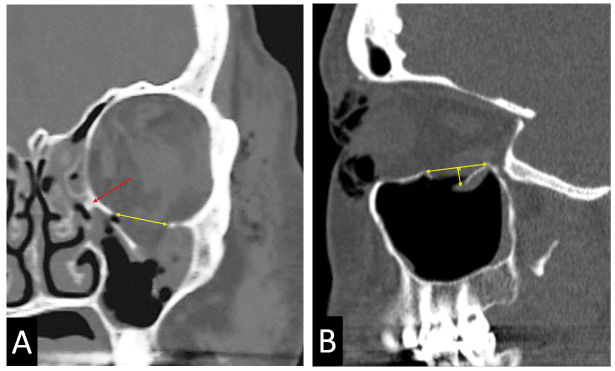
Orbital floor fracture with significant soft tissue entrapment a so called trapdoor fracture.
Direct orbital floor fracture.
The orbit is one of a pair of bony cavities each housing the globe and associated structures.
Orbital blowout fractures seen in the emergency setting commonly occur after trauma.
Inferior blowout fractures are the most common.
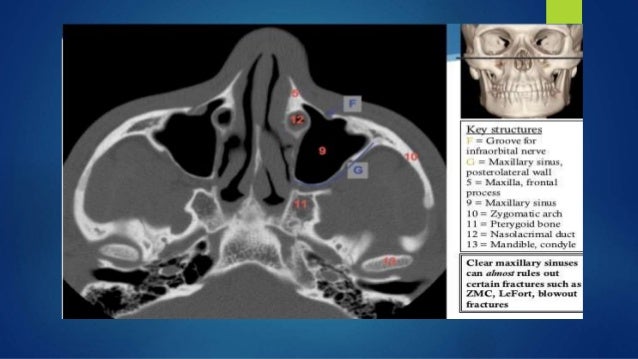
A study by huang et al indicated that in patients with head trauma lack of maxillary hemosinus on conventional head ct scanning predicts the absence of orbital floor fracture the negative.
The floor is usually the path of least resistance and fractures downward into the maxillary sinus.
Blowout fractures can occur through one or more of the orbital walls.
The orbit is formed by 7 bones.